It is easier to consider blockchain the newest fad than wrap the head around jargons such as distributed ledger technology. We totally get it.
But we don’t want that for you anymore.
Not when blockchain has evolved from being a futuristic technology that was touted to change the world to being the revolution that is already spreading its magic.
Starting with the basics
Bitcoin has got the whole world pumped at the moment.
Our maximum exposure to the word “blockchain” comes from seeing it being associated with bitcoin. This has left a lot of people confused about the difference between the two.
With everyone talking about it, we’d like to help you join the conversation.
Bitcoin is a digital currency.
The breakthrough technology that enabled its creation is blockchain.
Bitcoin is the digital currency and blockchain is the technology on which it is built.
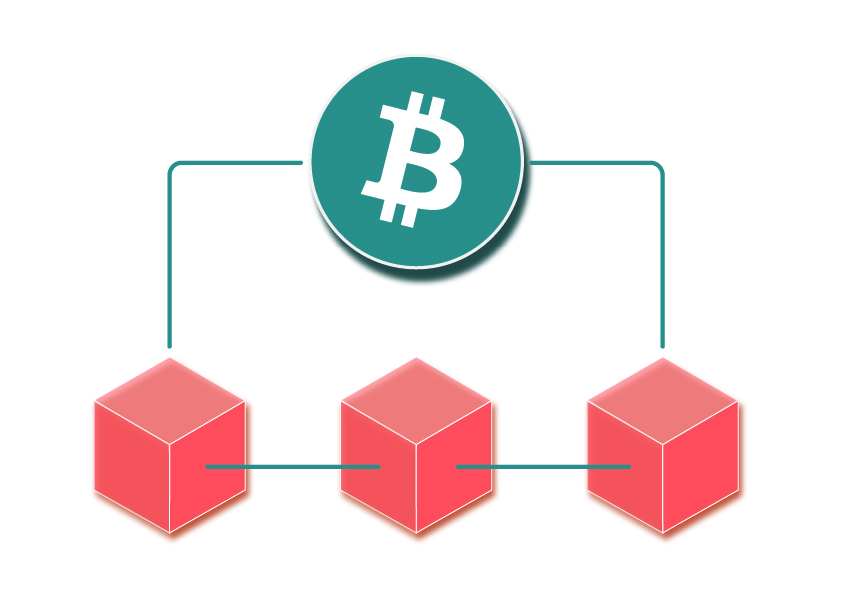
So whilst the world knows blockchain because of bitcoin, it is far from being its only use case.
Blockchain is a very powerful technology that stands to revolutionise the way we ACCESS, VERIFY and TRANSACT information, peer to peer, transforming industries and collaborations.
How does it work?
Blockchain works like a ledger (it records transactions).
A group of transactions forms a block.
As more transactions take place, a series of blocks are formed and linked, like a chain.
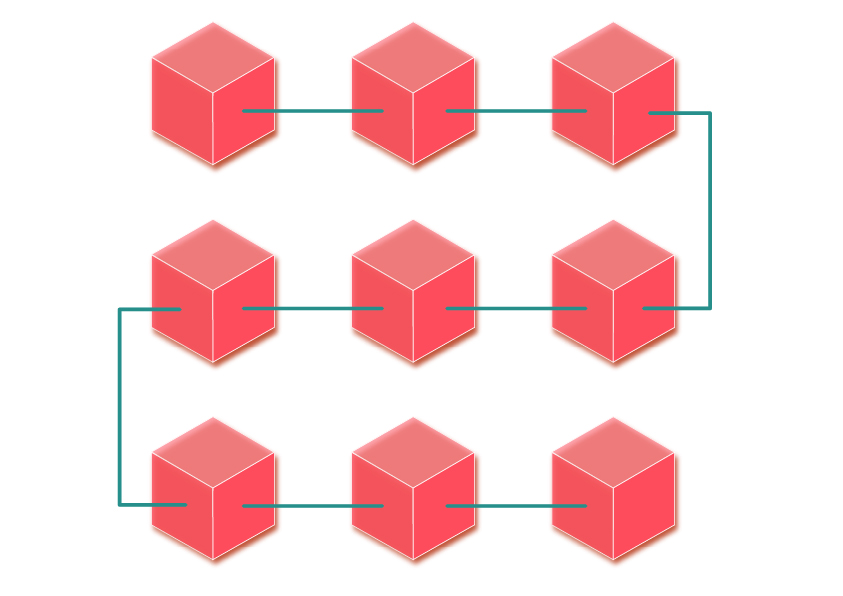
It is essentially a digital ledger of transactions that is duplicated and distributed across all the computer systems on the blockchain.
Each block in the chain contains a number of transactions, and every time a new transaction occurs on the blockchain, a record of that transaction is added to every participant’s ledger with an immutable cryptographic signature called a hash.
This means if one block in one chain were to be changed, it would be immediately apparent that it has been tampered with. If hackers wanted to corrupt a blockchain system, they would have to change every block in the chain, across all of the distributed versions of the chain.
How is it different from all other ledgers?
To understand the chief features of blockchain technology, let’s use a simple analogy.
I first wrote this article on Google Doc which I then shared with my two peers for review. When I shared the document, it was distributed, not copied or transferred. All three of us now have access to the document at the same time. No one is locked out awaiting changes from another party, while all modifications to the doc are being recorded in real-time, making changes completely transparent.
The whole point of using a blockchain is to let people — in particular, people who don’t trust one another — share valuable data in a secure, tamperproof way.
MIT Technology Review
It is a decentralised network
Generally, any ledger is stored in one central place. And the organisation that stores this data has access to all your information which they can use/tamper. Plus they have the added responsibility of keeping it secure to prevent any party with the wrong intentions from getting their hands on it.
But with the rising number of data breaches we’ve seen in the past, we can tell that this is a tougher task than it sounds.
Enter blockchain.
Blockchain uses a decentralised network. A connected set of computers that hold the ledger records and constantly reconcile transactions.
Most blockchains aren’t controlled by any one person or group, so the rules that govern it can’t be changed without the majority of people giving their permission.
This means that there is no single entity (like a government) that can control the ledger.
Having a blockchain publicly available helps create transparency. It is a data store where anyone can view and add new data, and existing data can’t be changed without everyone knowing.
You can trust the data
Blockchain helps people trade one-on-one and at scale. That is achieved by ensuring everyone can trust the data.
Before blockchain, ledgers could be tampered with. To keep them safe meant expensive protection and increasing cost of transactions.
In blockchain, each transaction is secured by cryptographic locks. This creates a record of truth that requires all participants to agree and approve.
This verification presents a far greater challenge to hackers than networks hosted from a central system and creates trust in the chain.
The data that is shared on a blockchain is thus authentic and tamper-free.
It removes the middleman
When our societies were small, it was easier for people to trade with each other because they trusted one other. As the societies grew, we invented intermediaries such as Airbnb, Uber, eBay, Amazon that acted as digital marketplaces that enabled exchange of value.
Trusted middlemen don’t come cheap or without influence.
Blockchain allows us to skip the middleman and transact directly, peer to peer. Interactions – purchases, exchanges of data, or anything else – that happen on it are enforced by the system itself, instead of by a third party. That means you don’t have to trust a person, company, or government, but you can still trust that your interaction will happen.
This is big.
It helps speed up the pace and reduce the cost of transacting just about everything.
Why would a business enterprise look for a blockchain solution?
Blockchain helps build trust in the supply chain. Blockchain might be adopted by certain enterprises to:
Process data efficiently
A blockchain platform serves as a digital layer for the processing and coordination of information. The distributed architecture and consensus mechanisms of blockchain networks facilitate more efficient data coordination than paper-based and centralised systems.
Have trusted transactions and secure business networks
The unique design of a blockchain ensures an immutable record of transactions that all network participants can trust. Moreover, smart contracts enable the automation of business logic, simplifying reconciliation across complex business networks.
Create, issue, and manage digital assets
The digitization of goods and assets has emerged as one of the most exciting business applications of blockchain technology.
Quick view at some of the use cases
If you want a diamond ring, you might want to make sure the diamond is from a conflict-free mine and was not involved in a shady transaction.
Everledger created the Diamond Time Lapse using blockchain to securely track, trace and authenticate the provenance of diamonds. Over the last 3 years, it has tracked the entire lifetime journey of 2 million diamonds. This means you can see the journey of the diamond all the way from the mine to cutting to the store.
——————————————————————————————————————–
Sending money among countries in Africa can be slow, expensive and volatile. Less developed banking systems get in the way of doing business.
Bit Pesa is a blockchain-based payment platform that’s trying to reduce the cost and increase the speed of business payments to, from, and within sub-Saharan Africa, making it easier for African countries to trade with the rest of the world.
——————————————————————————————————————–
More than 12 million refugees are currently displaced due to war and conflicts in the Middle East.
Many agencies are giving refugees the ability to have their health records stored on blockchain in the future to record and access quick and quality healthcare without being affected by lack of records or language barriers.
——————————————————————————————————————–
While blockchain is still relatively new and many experiments will fail before they succeed, the possibilities for innovation are endless. We’ll see industries such as banking and payments, cybersecurity, government, crowdfunding, healthcare, employment verification, rentals and ride-sharing etc. evolve into preparing autonomous solutions both in business and our personal lives.
Sooner we start viewing blockchain away from the eyes of cryptocurrencies and get-rich-quick schemes, better it will be for us to realise its enormous potential to do safe, transparent and scalable transactions.



0 Comments